Implementasi Struktur Data Graph Pada Java
picture from here
Struktur Data Graph
Graph merupakan salah satu jenis struktur data non linier yang terdiri dari beberapa node atau vertex yang saling terhubung dengan beberapa vertex lainnya oleh suatu ikatan yang disebut dengan edge. Graph merepresentasikan bagaimana hubungan antara satu vertex dengan vertex lainnya, seperti pada jaringan komputer yang menjelaskan bagaimana komputer satu dapat terhubung dengan komputer lainnya.
Implementasi Graph Menggunakan Java
Berikut ini merupakan implementasi graph menggunakan java
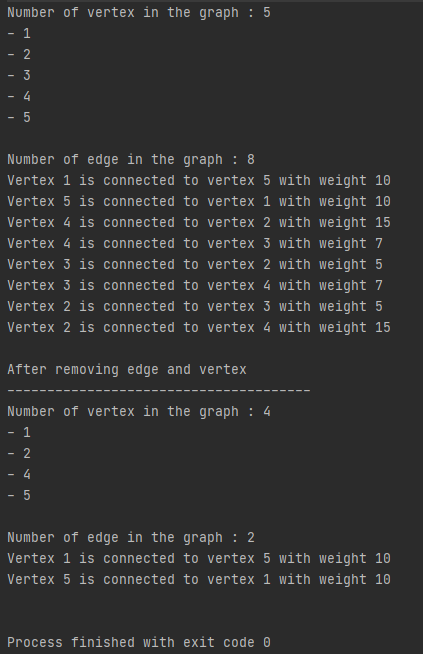
Jika class MainApplication di run, maka hasilnya akan seperti berikut
Source code dari program di atas dapat diakses di sini
Comments
Post a Comment